Basic electronic components
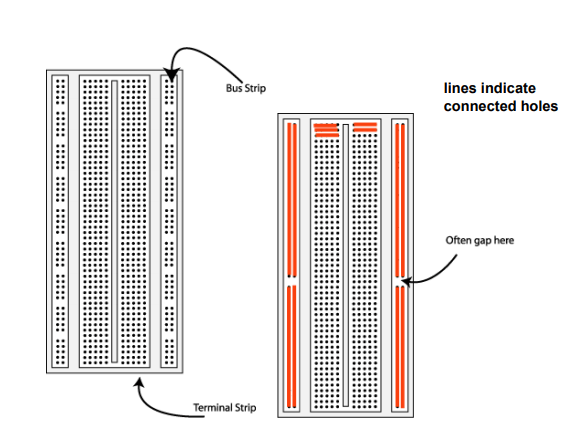
Breadboard- used for prototyping circuits:
1. Resistor
• Description: A resistor is a passive electrical component that limits or regulates the flow of electrical current in a circuit. It provides a specific amount of resistance, measured in ohms (Ω).
• Function: Used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, divide voltages, and terminate transmission lines.

2. Capacitor
• Description: A capacitor is a passive component that stores energy in an electric field. It consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material called the dielectric.
• Function: Used for energy storage, filtering, and signal coupling/decoupling in electronic circuits.

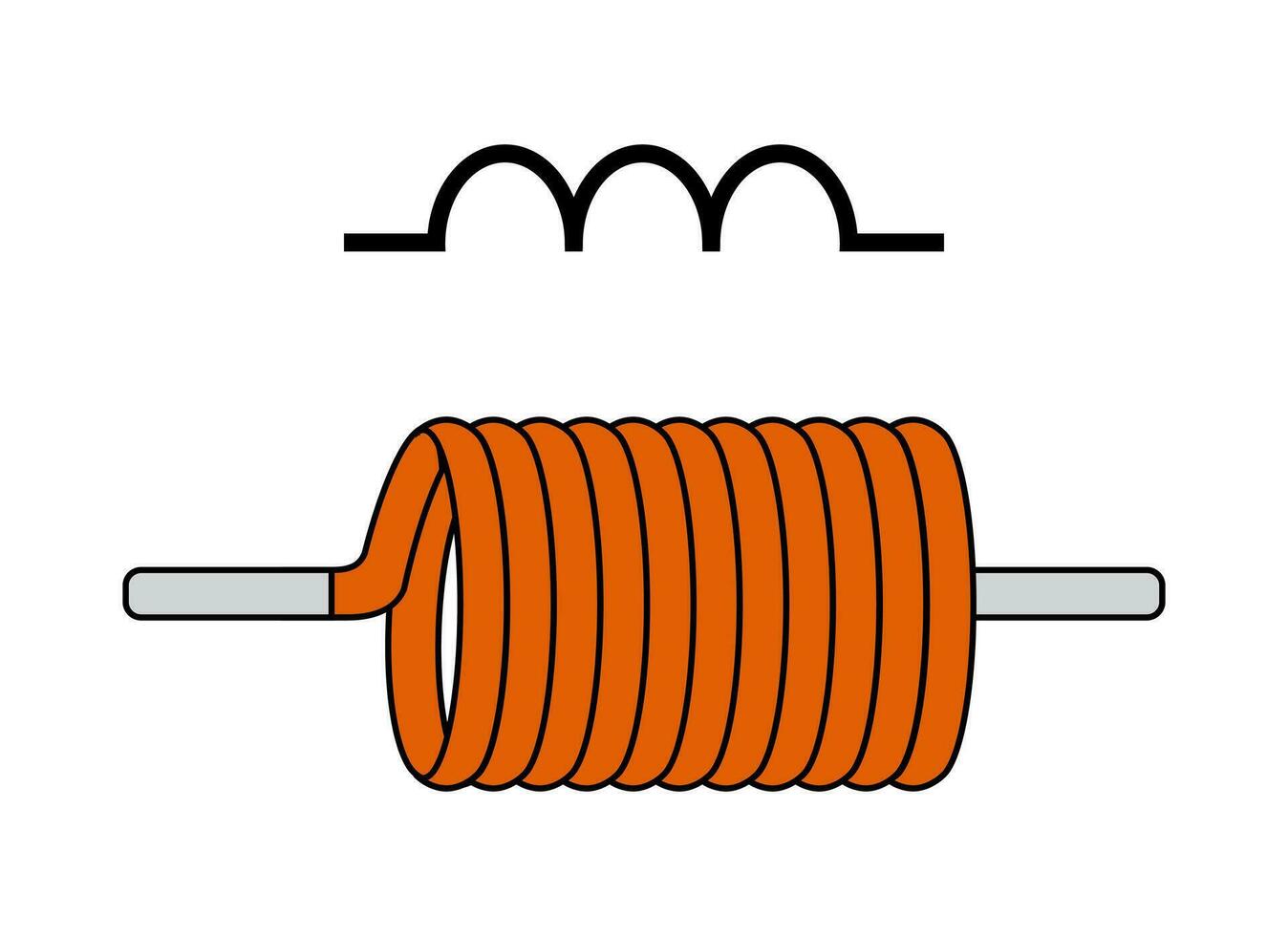
3. Inductor
• Description: An inductor is a passive component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electrical current flows through it. It typically consists of a coil of wire.
• Function: Used in filtering applications, energy storage in power supplies, and in tuning circuits.
4. Diode
• Description: A diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in one direction only. It has low resistance to current flow in one direction and high resistance in the opposite direction.
• Function: Used for rectification (converting AC to DC), protection (e.g., voltage spikes), and signal demodulation.

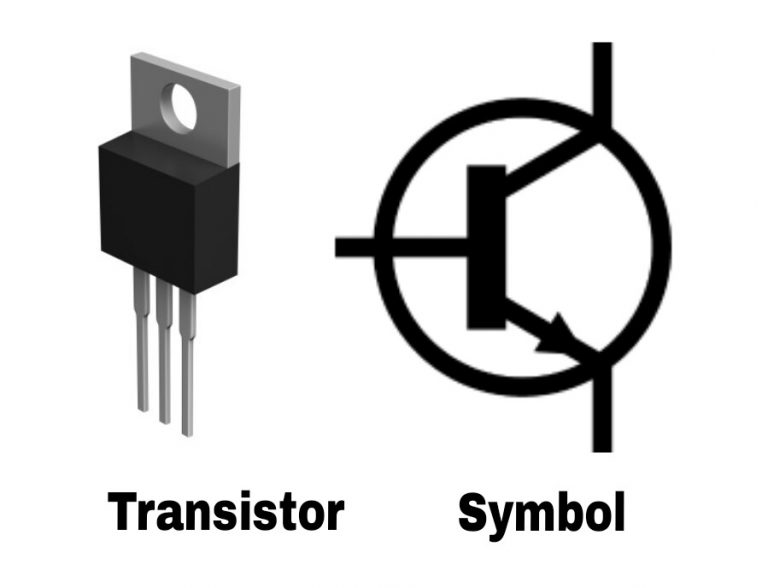
5. Transistor
• Description: A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. It consists of three layers of semiconductor material.
• Function: Used in amplification, switching, voltage regulation, and signal modulation.
6. LED (Light Emitting Diode)
• Description: An LED is a semiconductor light source that emits light when current flows through it. It is a type of diode that emits light when activated.
• Function: Used for indication, display, and lighting purposes.
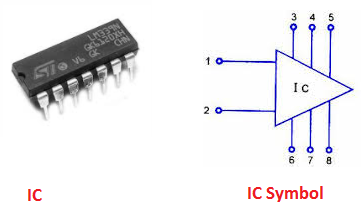
7. Integrated Circuit (IC)
• Description: An IC is a set of electronic circuits on a small flat piece (or “chip”) of semiconductor material, usually silicon. It can contain millions of tiny components like transistors, resistors, and capacitors.
• Function: Used in virtually all electronic equipment today, including computers, mobile phones, and other digital appliances.
8. Switch
• Description: A switch is a device that can open or close an electrical circuit, interrupting the current or diverting it from one conductor to another.
• Function: Used to control the flow of current in a circuit, allowing it to be turned on or off.

9. Battery
• Description: A battery is a device consisting of one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy.
• Function: Used as a power source for portable electronic devices and in power backup systems.

10. Fuse
• Description: A fuse is a safety device that protects electrical circuits by melting and breaking the circuit when excessive current flows through it.
• Function: Used to prevent damage to electronic components and reduce the risk of fire.
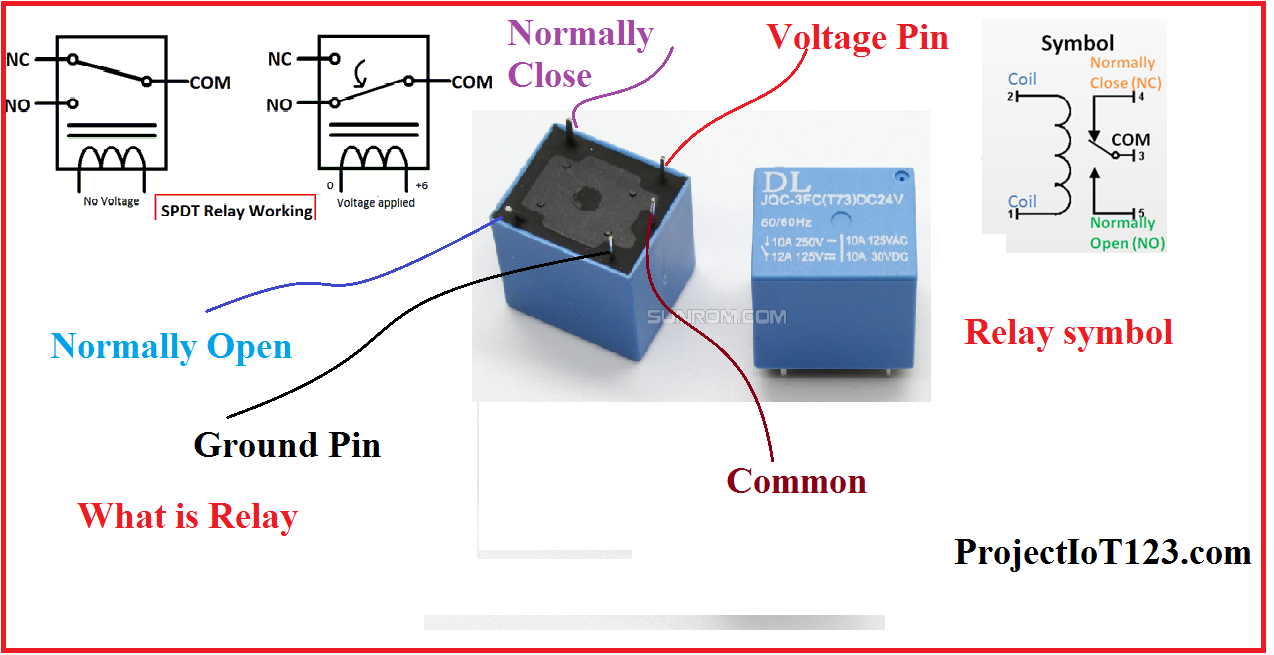
11. Relay
• Description: A relay is an electrically operated switch that uses an electromagnet to mechanically operate a switch.
• Function: Used to control a high-power circuit with a low-power signal.
12. Potentiometer
• Description: A potentiometer is a three-terminal resistor with a sliding or rotating contact that forms an adjustable voltage divider.
• Function: Used to adjust levels of electrical signals, such as volume control in audio equipment.
These components form the foundation of most electronic circuits, enabling the design and functioning of a wide range of electronic devices and systems.